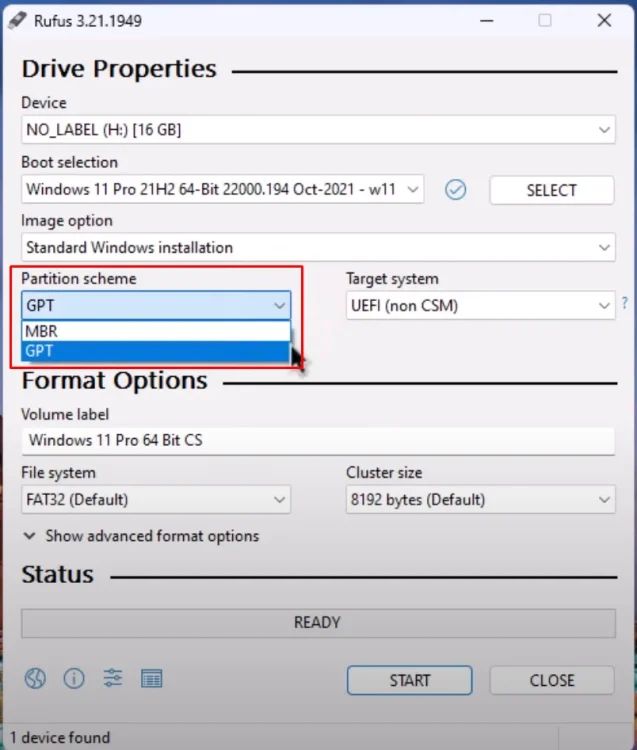
💾 GPT vs. MBR: What’s the Difference When Making a Bootable Drive?
If you’ve ever created a bootable USB or installed an OS, you’ve likely come across GPT and MBR partition schemes. But what’s the real difference — and which one should you use?
🔹 MBR (Master Boot Record)
Legacy partition style (since 1983)
Supports up to 4 primary partitions
Max disk size: 2 TB
Works with BIOS systems
🔹 GPT (GUID Partition Table)
Modern standard (part of UEFI)
Supports 128+ partitions
Max disk size: Zettabytes+
Required for booting with UEFI systems
⚙️ When to Use What:
💻 Use MBR: Installing older OS (Windows 7 or earlier), or if your system uses legacy BIOS
🚀 Use GPT: For modern systems with UEFI firmware, larger drives, and better redundancy
🧠 Pro Tip:
To check your system type: Run msinfo32 → Look for “BIOS Mode: UEFI/Legacy”
Choosing the right scheme ensures compatibility, faster boot times, and better disk management.
🔹 MBR (Master Boot Record)
Legacy partition style (since 1983)
Supports up to 4 primary partitions
Max disk size: 2 TB
Works with BIOS systems
🔹 GPT (GUID Partition Table)
Modern standard (part of UEFI)
Supports 128+ partitions
Max disk size: Zettabytes+
Required for booting with UEFI systems
⚙️ When to Use What:
💻 Use MBR: Installing older OS (Windows 7 or earlier), or if your system uses legacy BIOS
🚀 Use GPT: For modern systems with UEFI firmware, larger drives, and better redundancy
🧠 Pro Tip:
To check your system type: Run msinfo32 → Look for “BIOS Mode: UEFI/Legacy”
Choosing the right scheme ensures compatibility, faster boot times, and better disk management.